Ovarian cyst: prevention, treatment, cancer risk
According to statistics, in 70% of women in different periods of life, gynecologists diagnose cysts of various etiologies. What is an “ovarian cyst”? How is an ovarian cyst treated? And what does a woman need to know when she hears a diagnosis of ovarian cyst?
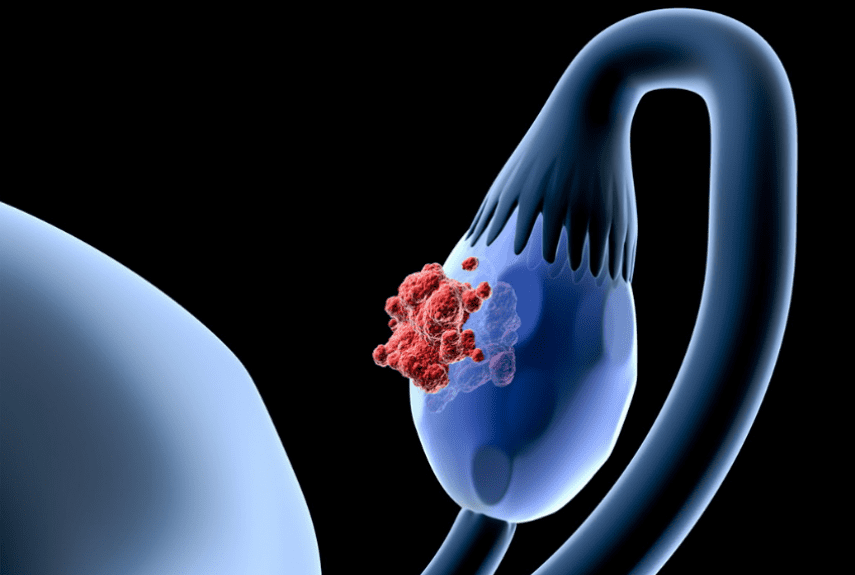
An ovarian cyst is a fluid containing mass in the ovary. The word “cyst” itself comes from the Greek. “Kystis” meaning “bubble”. Today, many women are diagnosed with an ovarian cyst: they contact us with this problem every day. Today there are many factors that contribute to the formation of ovarian cysts – heredity, ovarian dysfunction, decreased immunity, ecology, bad habits, stress, frequent flights, etc.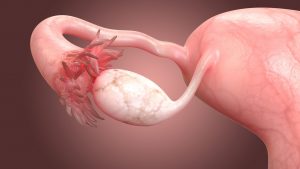
Most often, the presence of ovarian cysts is diagnosed during ultrasound of the pelvic organs, and is also detected during ultrasound examinations of the abdominal organs. A cyst can be detected not only by a gynecologist, but also by related specialists – therapists, surgeons, urologists, whom women turn to because of pain in the abdomen. Such pain can be similar to pain caused by appendicitis or intestinal colic.
You need to know! The following symptoms are characteristic of an ovarian cyst:
If you feel severe pain in the lower abdomen – seek medical attention in the near future – these symptoms may be characteristic of torsion or rupture of an ovarian cyst.
The presence of painful sensations during intercourse and during physical exertion can also be a symptom of ovarian cysts.
Be sure to pay attention to menstrual irregularities – delays in menstruation and intermenstrual bleeding – they may also indicate the presence of an ovarian cyst.
An ovarian cyst is a common cause of urinary problems.
Why are ovarian cysts dangerous? How are they treated?
Before prescribing treatment for an ovarian cyst, it is necessary to determine its etiology. Most often, gynecologists perform ultrasound diagnostics, which gives high-precision results. Also, the gynecologist can send the patient for an additional examination to obtain additional information to determine the etiology of the cyst – to pass an analysis for tumor markers, as well as to undergo MRI diagnostics.
Today, gynecologists distinguish 2 main types of cysts: true and functional, the appearance of which is associated with a woman’s hormonal background.
Functional cyst
If a functional cyst is found, a specific treatment is prescribed, as well as a re-examination after menstruation. Very often, a functional cyst is represented by a “corpus luteum cyst”, which forms after ovulation and independently undergoes reverse development without requiring additional treatment. Follicular cysts are also a type of functional cyst – they can go away on their own after menstruation.
True cyst
True cysts are a serious condition that requires treatment. True cysts can cause pain, torsion, rupture, growth and degeneration into a malignant tumor.
True cysts are of the following types:
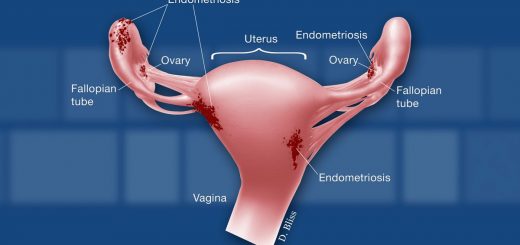
Endometrioid cyst is a cyst that, in the absence of timely treatment (surgery), leads to infertility. An endometrioid cyst is located in the ovary. During menstruation, the cells of the endometrioid cyst produce menstrual blood, which accumulates inside the cyst. As a result of this process, endometrioid cysts can grow to a large size, which can lead to rupture of the cyst. Such a cyst “squeezes” the healthy tissue of the ovary, which contributes to the disappearance of follicles and leads to infertility. Also, one of the serious complications of an endometrioid cyst is its rupture, during which the contents of the cyst (endometrial cells) enter the small pelvis and abdominal cavity, causing a serious disease – external endometriosis – which is characterized by constant pain, is difficult to treat and can lead to infertility. That is why such cysts need to be operated urgently in order to avoid serious consequences. After an operation to remove such a cyst, we always recommend that women plan a pregnancy in the near future.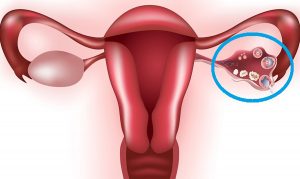
Cystadenoma is a true ovarian cyst. There are mucinous and serous cystadenomas. The main danger of cystadenomas is their high potential for malignancy, therefore, if this type of cyst is detected, the gynecologist prescribes surgical treatment.
Dermoid cyst. It is represented by the rudimentary elements of the adnexal tissues of the body, which are formed in the process of development. A feature of such cysts is slow but constant growth. A dermoid cyst can grow large, exert pressure on adjacent organs, and cause abdominal pain. The content of dermoid cysts can be fragments of bones, hair, teeth, adipose tissue, which are immersed in a viscous liquid and surrounded by a thick dense membrane.
How is the operation to remove an ovarian cyst performed?
Today we have all the possibilities to perform endoscopic treatment – a laparoscopic operation, which is performed through several punctures in the navel and ileal area. The operation lasts from 30 minutes to 1 hour, is carried out under general anesthesia, during the operation only the capsule of the cyst is removed while preserving the ovary. In the future, the removed material is sent for histological examination to identify the etiology of the cyst and the appointment of appropriate treatment. Operations to remove cysts are easily tolerated by patients, after the operation, women feel good, a few hours after the operation they are allowed to get up. You can return to your usual activities the next day after the operation.
Are there preventive measures to prevent cyst formation? Are there any relapses?
In case of pain, menstrual irregularities, women should consult a specialist in a timely manner. It is also necessary to undergo a medical examination once a year: during an appointment with a gynecologist, an ultrasound scan of the pelvic organs, mammary glands is performed, tests, smears for flora, oncocytology are taken, if necessary, examination for latent genital infections and blood for tumor markers.
Regarding recurrent cysts https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cyst, the risk of recurrent cysts is quite high. Only timely examinations and an attentive attitude to one’s body are able to diagnose and solve the problem in time.